

Did you know humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas? Does that make us part-banana? No, but it’s fascinating to know how DNA, the blueprint of life, is responsible for our makeup. From our appearance to the gamut of emotions we experience, DNA is essentially the regulating block for what we call ‘genes’.
DNA – WHAT IS IT?
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid (try saying that five times fast) is primarily responsible for determining your physical appearance and behavioral traits. This genome provides the coding for the different physical and physiological processes for all living organisms. Consisting of four building blocks or bases including thymine, adenine, cytosine and guanine, this double-stranded structure forms the genetic hereditary unit allowing specific
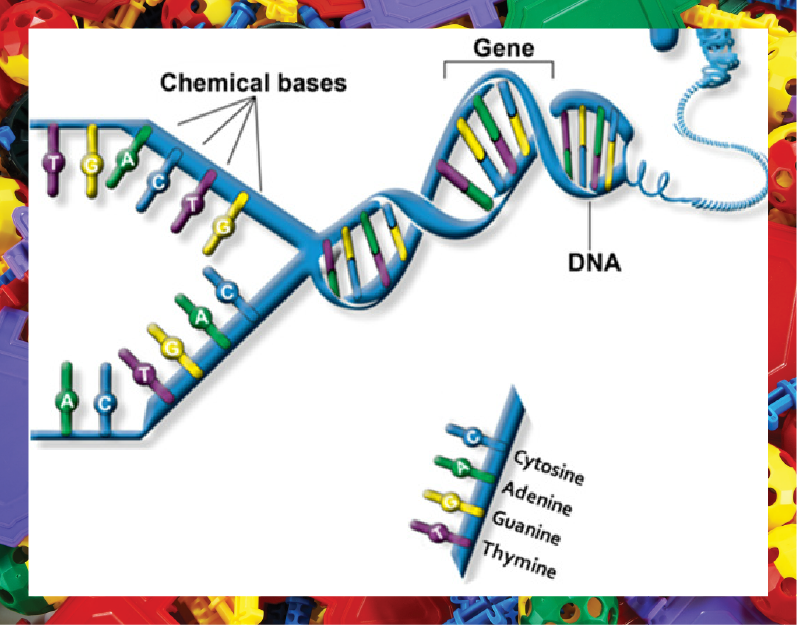
attributes or characteristics to be passed on from parents to their offspring.
The bases on a single strand of the DNA molecule form a pair with a complementary base on the opposite strand in the double helix structure. This results in a unique DNA ladder where the base-pairs are joined by hydrogen bonds to form the rungs of the ladder. The sequence of these base-pairs contains instructions or genetic code. The human genome is composed of 3.2 billion bases of DNA and contains the directions for making all the proteins in our body.
WHAT YOUR DNA CAN DETERMINE

SEX
One of the simplest things your DNA can tell about you is gender. DNA tests are conducted at times to find out whether someone is a male or female but this is often not required. You don’t need to look at a DNA sequence or the order of the base-pair to find out if your child would be a boy or a girl. All you require is a check for the X or Y chromosomes for a male and a pair of Xs for a female. A fetus normally grows as a female, by default, unless the gene is SRY, in which case it will be male.
HAIR COLOR
DNA can determine whether you’ll be a brunette, blond or redhead. The genome also determines the hair color pigmentresponsible for different hair colors. The gene instructs two pigment-producing cells to make eumelanin and pheomelanin to give hair its color.Eumelanin corresponds to two subtypes of black or brown shades, determining the darkness of the hair color. While all humans have a little pheomelanin in their hair, the pigment gives all redheads the shades orange and red.
EYE COLOR
The eye color is determined by four different genes. It was initially thought eye color is was simply passed on by recessive and dominant parts of a gene, but it is now understood to be the result of a far more complex inheritance pattern. Scientists can study the combination of genes to determine the eye color of any individual from the three primary groups, light (blue and grey), hazel or dark (black and brown).
LONG LIFE
A specific version of the Klotho gene can be explored to study the longevity of human life since it is associated with our life-span. The gene has an impact on various health conditions such as coronary heart disease and other cardio-renal diseases. It can be used to gain an insight into the life-time of any individual depending on the health conditions.
THE FUTURE OF DNA RESEARCH
Recent advances in science have led to breakthrough discoveries in DNA and genealogy. Researchers at the Oregon Health and Science University, for example, used gene-editing tool CRISPR-Cas9 to fix a mutation responsible for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a genetic heart disease. Using this technology, the embryos can correct the mutation themselves with timely input from the healthcare practitioners, so the genetic illness does not pass on to future generations.
Advancements in forensic DNA profiling, DNA research and genetic science have been significant for the human race and will continue to benefit us in the future as well. As author Sam Kean says, “Genes are like the story, and DNA is the language that the story is written in”. As important as the study of DNA is, it’s still rather startling to know we happen to share our story with bananas.









Trackbacks/Pingbacks